2013年考研《英语》考前押密试卷(二)
-
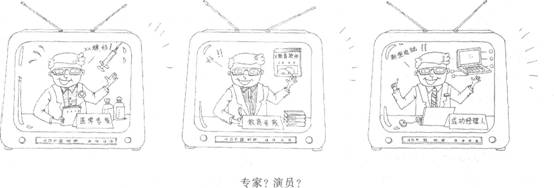
Write an essay of about 160-200 words based on the following drawing. In this.essay,
you should :
1 ) describe the pictures briefly,
2) interpret the meaning, and
3) give your comment.
You should write neatly on ANSWER SHEET 2. (20 points)
-
Jordan is one of your business partners. Recently he was promoted to be the General Manager of ECC Company. Write a letter to
1 ) congratulate him on his promotion and
2) express your wish to cooperate with him.
You should write about 100 words on ANSWER SHEET 2. Do not sign your own name at the end of the letter. Use "Li Ming" instead. You don't have to write the address. (10 points)
-
__________。
-
__________。
-
__________。
-
__________。
-
__________。
-


根据以上内容,回答1~5题。
__________。
-
__________。
-
__________。
-
__________。
-

41.Speaking to someone you know well.

42. Howold are your listeners?
43. Sexcomposition of your listeners.
44.Interest in topic.
45.Interests or hobbies of the listeners.
[A] If you're invited to speak to awomen's or men's organization, you know the answer to this question at once.Quite often, however, audiences are mixed fairly evenly, although at times onesex may predominate.
[B] Do members of your prospectiveaudience spend evenings watching TV movies and drinking beer at a local tavern,or do they read the Harvard Classics and attend concerts of Beethoven andMozart? Do they play bingo and 21, or do they pursue the questions the intriguingintricacies of contract bridge and chess? Answers to these questions can helpyou choose the most appropriate material and language for your audience. Yourchoices can be crucial in determining the success or failure of yourpresentation.
[C] Are the members recent collegegraduates, senior citizens, or business executives in midcareer? Just remember,age exerts a powerful impact on people's attitudes, values and motivations.
[D] For example, your departmentmanager may ask you to explain and demonstrate a procedure to some fellowemployee. Or she may select you to address your department on behalf of thelocal blood donor drive. In both speech situations--in class and on thejob--you're familiar with your audience; you speak their language; you havethings in common with them.
[E] Are you aware of the educationalbackground of your audience? How many of them have doctoral degrees, masterdegrees or bachelor degrees? This will decide what kind of language you shouldadopt and how much they can understand.
[F] Are the members of theorganization interested in the topic or are they required to attend regardlessof their interest? If the latter is true, what types of material will mostlikely pique their curiosity?
根据以上内容,回答1~5题。
__________。
-
Wec
- an learn from the last two paragraphs that [A] it might
- be diffi
- cult to completelyshake off one's ol
- d identities. [B] people hate to have thumbnaildescriptions of themselves. [C] it might take additional work forpeople to entirely forget their past. [D] people hate to hear their school
-
Psychologists seem to believe th
- at if adults want to remake their identity,they need to [A] tell their psychologists very similarstories a
- bout themselves. [B]
- comman
- d the identity-forming factorsthemselves. [C] quit their jobs and start their ownbusiness. [D] hire a wonderful tutor to getthemselves into the honor roll.
-
The
- author mentioned Houdini in the text to [A] tell readers how he treated thepadlocked
- boxes. [B] introdu
- ce the topic of IQ
- differences between siblings. [C] illustrate the point that previousidentities can be remade. [D] explain how to sharpen one'spsychological skills.
-
According to the text, one c
- an expand one's identity [A]
- by finding a way to stay away fromone's family and
- community. [B] by combining late-night bullsessions with backyar
- d barbecues. [C] by consulting a professionalpsycho-therapist. [D] by playing various online computergames with new acquaintances.
-


根据以上内容,回答16~20题。
- Arecent study shows that [A] the firstborns and younger siblingsare often treated differently. [B] higher IQ holders in a family arealways the eldest. [C] the firstborns in a family ofte
-
Itc
- an inferred from the passage that [A] 1150 CEOs have
- benefited finan
- ciallyfrom lucky grants. [B] more than 850 CEOs owe their successto mere luck. [C] opportunistic timing can provi
- deunfair financial rewards. [D] lucky grants are widely spread overvarious industries.
-
Theresult of the
- author's study shows that [A] stock options are more likely to
- beawarded when pri
- ces are low. [B] there is a vague relationship betweenstock options an
- d grant price. [C] there is a clear relationship betweenlucky grants and lucky dates. [D] stock options are only awarded whenthe price is at the lowest.
-
According to the
- author, the Sar
- banes-Oxley A
- ct [A] effectively eliminate
- d the practiceof backdating. [B] leads to a larger percentage oflucky grants. [C] guarantees that grants are reportedimmediately. [D] helps to reduce the incidence oflucky grants.
-
Them
- ain purpose of the author's study is to find out [A] how the company's stock price went upafter the grant date. [
- B] how sto
- ck price
- distributioninfluence the rank of granted price. [C] how backdating practices influencethe value of stock shares. [D] how the granted price ranked in themonth of the grant. &
-


根据以上内容,回答11~15题。
- According to the passage, more stock-options were granted to executives because [A] responsibilities increase very faston the shoulders of the executives. [B] they account for a very importantpart in executive
-
We c
- an learn from the last paragraph that [A] practicing yoga can havepractical military uses. [
- B] soldiers need to be fo
- cuse
- d inimportant missions. [C] yoga will soon become a part ofSEAL basic training. [D] military trainings should designyoga into their program.
-
According to Steffens, pr
- acticing yoga [A] helps exercisers remain young. [
- B] is very effe
- ctive in relievingback pains. [C]helps exercisers realize thepotentials of their bo
- dies. [D] are good for forming a habit ofdoing things in a regular pattern.
-
Trieger seems to believe th
- at [A] practicing yoga can providesoldiers with some sort of relief. [
- B] doing yoga poses in full
- combatgear is shocking for sol
- diers. [C] soldiers should be peaceful instead of being too masculine. [D] military practices of yoga shouldbe done with closer inspection.
-


根据以上内容,回答6~10题。
- Alan thought it is difficult to explainthe scene to his fellow Marines because [A] yoga is a peaceful meditationprocess. [B] yoga is thought to be a littlefeminine. [C] only women would
-
Wec
- an infer from the passage that yoga [A] has
- been popular ever sin
- ce itsa
- dvent in India. [B] is an ancient Hindu practice ofmeditation. [C] focuses on improving muscularstrength. [D] is becoming increasingly popularamong soldiers.
-
The
- author's attitude towards this issue of using nuclear weapons against Japanseems to
- be &
- critical. [C] supportive. [
- D] objective.
-
Wec
- an infer from the last paragraph that [A] scientific knowledge and technicaladvance may lead to mass destruction. [
- B]
- cooperation by scientists will oftenresult in technical a
- dvances. [C] nuclear weapons have made normal,intelligent people crazy. [D] nuclear weapons were more powerfulthan. expected.
-
Itis implied in the p
- assage that western people at the time [A] were indifferent to the deaths ofthe civilians in an enemy country. [
- B] were sympatheti
- c with the
- deaths ofthe Japanese civilians. [C] were taking a justifiable revengeon the Japanese troops. [D] were intimidated when hearing aboutthe death in Japan.
-


根据以上内容,回答1~5题。
- According to the passage, nuclear weapons were initially designed to [A] force Japan to surrender in theSecond World War. [B] end the war with Germany in theSecond World War. [C] take a
-
According to the second p
- aragraph, nuclear weapons are not necessary
- be
- cause [A] the Japanese have a limite
- d amount ofnatural resource. [B] the US could find other ways toforce Japan to surrender. [C] the people in Hiroshima and Nagasakiare innocent. [D] the Japanese rulers were alreadynegoti
-
__________。
[
- A] gives&n
- bsp; [B] giving [
- C] to give [
- D] give
-
__________。
[
- A] newspapers&n
- bsp; [B] books [
- C] me
- dia [D] periodicals
-
__________。
[
- A] always&n
- bsp; [B] never [
- C] sel
- dom [D] hardly
-
__________。
[
- A] negative&n
- bsp; [B] positive [
- C] para
- doxical [D] controversial
-
__________。
[
- A] prevent&n
- bsp; [B] explore [
- C] prohibit [
- D] generate
-
__________。
[
- A] admired&n
- bsp; [B] admitted [
- C] ab
- dicated [D] adhered
-
__________。
[
- A] at&n
- bsp; [B] in [
- C] on [
- D] for
-
__________。
[
- A] Given&n
- bsp; [B]
- Consi
- dering [C] Barring [D] Concerning
-
__________。
[
- A] which&n
- bsp; [B] where [
- C] when [
- D] what
-
__________。
[
- A] lead to&n
- bsp; [B] point to [
- C] come to [
- D] turn to
-
__________。
[
- A] dedicated&n
- bsp; [B]
- concerne
- d [C] engaged [D] preoccupied
-
__________。
[
- A] devoted&n
- bsp; [B]
- confuse
- d [C] sensible [D] isolated
-
__________。
[
- A] contaminated&n
- bsp; [B]
- containe
- d [C] sustained [D] maintained
-
__________。
[
- A]
- but [B] so [
- C] for [
- D] as
-
__________。
[
- A]
- benefit [B] derive [
- C]
- differ [D] deviate
-
__________。
[
- A] fewer&n
- bsp; [B] more [
- C] less [
- D] much
-
__________。
[
- A] variety&n
- bsp; [B] me
- chanism [C] monotone [
- D] conformity
-
__________。
[
- A] in particular [
- B] in general [
- C] at least [
- D] by contrast
-
__________。
[
- A] So&n
- bsp; [B] Yet [
- C] Once [
- D] Since
-

根据以上内容,回答1~20题。
__________。
[A] when
[B] that
[C] which
[D] where













