下面程序实现十进制向其他进制的转换。
[Java程序]
C1ass Node{
int data;
Node next;
}
class Transform{
private Node top;
publiC void print(){
Node P;
while(top !=null){
P=top;
if(P.data>9)
System.out.print((char)(p.data+55));
else
System.out.print(p.data);
top=P.next;
}
}
public void Trans(int d,int i)(//d为数字;i为进制
int m;
(1) n=false;
Node P;
while(d>0){
(2) ;
d=d/i;
P=flew Node();
if( (3) ){
P.data=m;
(4) ;
top=P;
n=true;
}
else{
p.data=m;
(5) ;
toP=P;
}
}
}
}
-
下面程序实现十进制向其他进制的转换。
[Java程序]
C1ass Node{
int data;
Node next;
}
class Transform{
private Node top;
publiC void print(){
Node P;
while(top !=null){
P=top;
if(P.data>9)
System.out.print((char)(p.data+55));
else
System.out.print(p.data);
top=P.next;
}
}
public void Trans(int d,int i)(//d为数字;i为进制
int m;
(1) n=false;
Node P;
while(d>0){
(2) ;
d=d/i;
P=flew Node();
if( (3) ){
P.data=m;
(4) ;
top=P;
n=true;
}
else{
p.data=m;
(5) ;
toP=P;
}
}
}
}
-
为参加网球比赛的选手安排比赛日程。
设有n(n=2k)位选手参加网球循环赛,循环赛共进行n-1天,每位选手要与其他n-1位选手赛一场,且每位选手每天赛一场,不轮空。试按此要求为比赛安排日程。
设n位选手被顺序编号为1,2,…,n。比赛的日程表是一个n行n-1列的表,i行j列的内容是第i号选手第j天的比赛对手。用分治法设计日程表,就是从其中一半选手(2m-1位)的比赛曰程,导出全体(2m位)选手的比赛日程。从只有2位选手的比赛日程出发,反复这个过程,直到为n位选手安排好比赛日程为止。
[C函数]
#include<stdio.h>
#define MAXN 64
int a[MAxN+1][MAXN];
void main()
{ int twoml,twom,il,j,m,k;
printf("指定n(n=2的k次幂)位选手,清输入k。\n");
scanf("%d",&k);
a[1][1]=2; /*预设2位选手的比赛日程*/
a[2][1]=1;
m=1;twoml=1;
while(m<k){
(1) ;
twoml+=twoml; /*为2m位选手安排比赛日程*/
(2) ;
/*填日程表的左下角*/
for(il=twoml+l;il<=twom;i1++)
for(j=1;j<=twoml-1; j++)
a[i1][J]=a[i1-twoml][j]+twoml;
(3) ;
for(i1=2;i1<=twom;i1++)a[i1][twoml]=a[i1-1][twom1]+l;
for(j=twoml+1;j<twom;j++){
for(i1=1;i1<twoml;i1++) a[i1][j]=a[i1+1][j-1];
(4) ;
}
/*填日程表的右下角*/
for(j=twoml;j<twom;j++)
for(ii=i;i1<=twoml;i1++)
(5) ;
for(i1=1;i1<=twom;i1++){
for(j=1;J<twom;j++)
printf("%4d",a[i1][J]);
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
-
下而程序实现十进制向其他进制的转换。
[C++程序]
#include"ioStream.h"
#include"math.h"
#include <conio.h>
typedef struct node{
int data;
node *next;
}Node;
class Transform
{
public:
void Trans(int d,int i); //d为数字;i为进制
void print();
private:
Node *top;
};
void Transform.:Trans(int d,int i)
{
int m,n=0;
Node *P;
while(d>0)
{
(1) ;
d=d/i;
p=new Node;
if(!n){
P->data=m;
(2) j
(3) ;
n++;
}
else{
p->data=m;
(4) ;
(5) ;
}
}
}
void Transform.:print()
{
Node *P;
while(top!=NULL)
{
p=top;
if(P->data>9)
cout<<data+55:
else
cout<<data;
top=p->next;
delete P;
}
}
-
函数Node *difference(A,B)用于求两个集合之差C=A-B,即当且仅当e是A中的一个元素,但不是B中的元素时,e是C中的元素。集合用有序链表实现,用一个空链表表示一个空集合,表示非空集合的链表根据元素之间按递增排列。执行C=A-B之后,表示集合A和B的链表不变,若结果集合C非空,则表示其链表根据元素之值按递增排列。函数append()用于在链表中添加节点。
[C函数]
typedef struct node{
int element;
struct node *link;
}Node;
Node *A,*B,*C;
Node *append(last,e)
Node *last;
int e;
{last->link=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
last->link->element=e;
return(last->link);
}
Node *difference(A,B)
Node *A,*B;
{ Node *c,*last;
C=last=(Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
while( (1) )
if(A->element<B->element){
last=append(last,A->element);
A=A->link:
}
else if( (2) ){
A:A->link;
B:B->link;
}
elSe
(3) ;
while( (4) ){
last=append(last,A->element);
A=A->link:
}
(5) ;
last=c;
c=c->link;
free(last);
return(c);
}
-
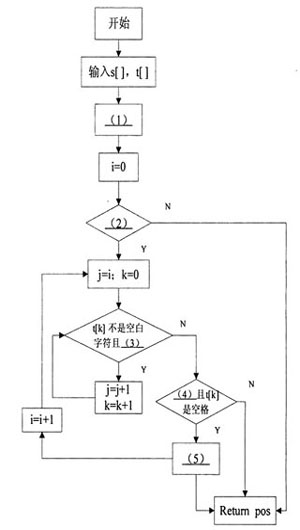
下面的流程图,用来完成求字符串t在s中最右边出现的位置。其思路是:做一个循环,以s的每一位作为字符串的开头和t比较,如果两字符串的首字母是相同的,则继续比下去,如果一直到t的最后一个字符也相同,则说明在s中找到了一个字符串t;如果还没比较到t的最后一个字符,就已经出现字符串不等的情况,则放弃此次比较,开始新一轮的比较。当在s中找到一个字符串t时,不应停止寻找(因为要求的是求t在s中最右边出现位置),应先记录这个位置pos,然后开始新一轮的寻找,若还存在相同的字符串,则更新位置的记录,直到循环结束,输出最近一次保存的位置。如果s为空或不包含t,则返回-1。
注:返回值用pos表示。
[问题]
将流程图的(1)~(5)处补充完整。
-
[说明1]
函数void convelt(chal *a,int n)是用递归方法将一个正整数n按逆序存放到一个字符数组a中,例如,n=123,在a中的存放为'3'、'2'、'1'。
[C函数1]
void convert(char *a,int n)
{ int i;
if((i=n/10)!=0; convert( (1) ,i);
*a= (2) ;
}
[说明2]
函数int index(char *s,char *t)检查字符串s中是否包含字符串t,若包含,则返回t在s中的开始位置(下标值),否则返回-1。
[C函数2]
int index(char *s,char *t)
{ int i,j=0;k=0;
for(i=0;s[i]!:'\0';i++)
( for( (3) ;(t[k]!='\0')&&(s[j]!='\0')&&( (4) );j++,k++);
if( (5) ) return(i);
}
return(-1);
}
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟练习题之单选题(1
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(2)
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(3)
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟试题及答案
高级经济师考试试题及答案:单选练习题
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(2)
