阅读以下程序说明和C++程序,将程序段中(1)~(5)空缺处的语句填写完整。
[说明]
C++语言本身不提供对数组下标越界的判断。为了解决这一问题,在以下[C++程序]中定义了相应的类模板,使得对于任意类型的二维数组,可以在访问数组元素的同时,对行下标和列下标进行越界判断,并给出相应的提示信息。
[C++程序]
#include <iostream.h>
template <class T> class Array;
template <Class T> class ArrayBody {
friend (1);
T* tpBody;
int iRows,iColumns, iCurrentRow;
ArrayBody(int IRsz, int iCsz) {
tpBody =(2);
iRows = iRsz;
iColumns = iCsz;
iCurrentRow = -1;
}
Public:
T& operator[] (int j) {
bool row_error, column_error;
row_error = column_error =false;
try {
if (iCurrentRow < 0 || iCurrentRow >= iRows)
row_error = true;
if (j<0 || j>= iColumns)
column_error = true;
if (row_error == true || column_error == true)
(3);
}
catch(char){
if (row_error == true)
cerr << "行下标越界[" << iCurrentRow << "]";
if (column_error = true)
cerr << "列下标越界[" << j << "]";
cout << "\n";
}
return tpBody[iCurrentRow * iColumns + j];
}
~Arraygody(){delete[]tpBody;}
};
template <class T> class Array {
ArrayBody<T> tBody;
Public;
ArrayBody<T> & operator[] (int i) {
(4);
return tBody;
}
Array(int iRsz, int iCsz) :(5) { }
};
void main()
{
Array<int> a1(10,20);
Array<double> a2(3,5);
int b1;
double b2;
b1 = a1[-5][10]; //有越界提示:行下标越界[-5]
b1 = a1[10][15]; //有越界提示:行下标越界[10]
b1 = a1[1][4]; //没有越界提示
b2 = a2[2][6]; //有越界提示:列下标越界[6]
b2 = a2[10][20]; //有越界提示:行下标越界[10]列下标越界[20]
b2 = a2[1][4]; //没有越界提示
}
-
阅读以下技术说明和Java代码,将Java程序中(1)~(5)空缺处的语句填写完整。
[说明]
类Queue表示队列,类中的方法如表4-12所示。
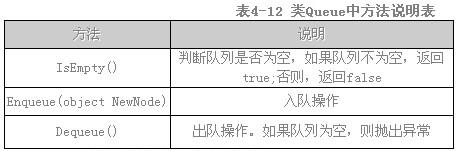
类Node表示队列中的元素;类EmptyQueueException给出了队列中的异常处理操作。
[Java代码]
public class testmain { //主类
public static viod main (string args[]) {
Queue q= new Queue;
q.enqueue("first!");
q.enqueue("second!");
q.enqueue("third!");
(1) {
while(true)
system.out.println(q.dequeue());
}
catch( (2) ) { }
}
public class Queue { //队列
node m_firstnode;
public Queue(){m_firstnode=null;}
public boolean isempty() {
if (m_firstnode= =null)
return true;
else
return false;
}
public viod enqueue(object newnode) { //入队操作
node next = m_firstnode;
if (next = = null) m_firstnode=new node(newnode);
else {
while(next.getnext() !=null)
next=next.getnext();
next.setnext(new node(newnode));
}
}
public object dequeue() (3) { //出队操作
object node;
if (is empty())
(4)
else {
node =m_firstnode.getobject();
m_firstnode=m_firstnode.getnext();
return node;
}
}
}
public class node{ //队列中的元素
object m_data;
node m_next;
public node(object data) {m_data=data; m_next=null;}
public node(object data,node next) {m_data=data; m_next=next;}
public void setobject(object data) {m_data=data; }
public object getobject(object data) {return m_data; }
public void setnext(node next) {m_next=next; }
public node getnext() {return m_next; }
}
public class emptyqueueexception extends (5) { //异常处理类
public emptyqueueexception() {
system. out. println ( "队列已空!" );
}
}
-
阅读以下程序说明和C++程序,将程序段中(1)~(5)空缺处的语句填写完整。
[说明]
C++语言本身不提供对数组下标越界的判断。为了解决这一问题,在以下[C++程序]中定义了相应的类模板,使得对于任意类型的二维数组,可以在访问数组元素的同时,对行下标和列下标进行越界判断,并给出相应的提示信息。
[C++程序]
#include <iostream.h>
template <class T> class Array;
template <Class T> class ArrayBody {
friend (1);
T* tpBody;
int iRows,iColumns, iCurrentRow;
ArrayBody(int IRsz, int iCsz) {
tpBody =(2);
iRows = iRsz;
iColumns = iCsz;
iCurrentRow = -1;
}
Public:
T& operator[] (int j) {
bool row_error, column_error;
row_error = column_error =false;
try {
if (iCurrentRow < 0 || iCurrentRow >= iRows)
row_error = true;
if (j<0 || j>= iColumns)
column_error = true;
if (row_error == true || column_error == true)
(3);
}
catch(char){
if (row_error == true)
cerr << "行下标越界[" << iCurrentRow << "]";
if (column_error = true)
cerr << "列下标越界[" << j << "]";
cout << "\n";
}
return tpBody[iCurrentRow * iColumns + j];
}
~Arraygody(){delete[]tpBody;}
};
template <class T> class Array {
ArrayBody<T> tBody;
Public;
ArrayBody<T> & operator[] (int i) {
(4);
return tBody;
}
Array(int iRsz, int iCsz) :(5) { }
};
void main()
{
Array<int> a1(10,20);
Array<double> a2(3,5);
int b1;
double b2;
b1 = a1[-5][10]; //有越界提示:行下标越界[-5]
b1 = a1[10][15]; //有越界提示:行下标越界[10]
b1 = a1[1][4]; //没有越界提示
b2 = a2[2][6]; //有越界提示:列下标越界[6]
b2 = a2[10][20]; //有越界提示:行下标越界[10]列下标越界[20]
b2 = a2[1][4]; //没有越界提示
}
-
阅读以下程序说明和C程序,将程序段中(1)~(7)空缺处的语句填写完整。
【说明】
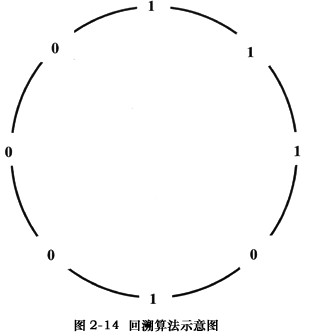
【C程序1】用回溯算法来产生由0或1组成的2m个二进位串,使该串满足以下要求。
视串为首尾相连的环,则由m位二进制数字组成的2m个子序列,每个可能的子序列都互不相同。例如,如果m=3,在串11101000首尾相连构成的环中,由3位二进制数字组成的每个可能的子序列都在环中恰好出现一次,它们依次是111,110,101,010,100,000,001,011,如图2-14所示。
【C程序2】是求“背包问题”的一组解的递归算法程序。“背包问题”的基本描述是:有一个背包,能盛放的物品总重量为S,设有N件物品,其重量分别为W1,W2,…,Wn,希望从N件物品中选择若干件物品,所选物品的重量之和恰能放入该背包,即所选物品的重量之和等于S。
【C程序1】
#define N 1024
#define M 10
int b [N+M-1]
int equal(int k, int j int m) {
int i;
for(i=0; i<m; i++
if ( b[ k + i] (1) )
return 0;
return 1; }
int exchange (int k, int m, int v){
while ( b[ k + m - 1 ) == v ) {
b[ kncm--i]=! v (2);
}
(3)=v;
return k;
}
init ( iht v) {
int k
for( k = 0;K = N + M - 1;k++)
b[k] = v;
}
main ( ) {
int m, v, k, n, j;
printf ('Enter m (l<m<10) , v v=0, v=1)\ n") ;
scanf (" %d%d , &m, &v);
n = 0x01 << m;
init (!v);
k=0;
while((4)< n)
for (j=0;j<k;j++)
if (equal (k, j, m)) {
k=exchange (k, m, v)
j=(5);
}
for (k= 0 ;k<n ;k++ )
print{ (" %d\ n" , b[k]) ;
}
}
【C程序2】
#include<stdio. h>
#define N 7
#define S 15
int w[N+1] = {0, 1, 4, 3, 4, 5, 2, 7};
int knap (int S, int n){
if (S == 0)
return 1;
if (s<0 || (s>0 && n<1))
return 0;
if ((6))) {
printf( "4d", w[n]);
return 1;
}
return (7)
}
main ( ) {
if (knap (S, N)
printf("OK:\n");
else
printf("NO!\n")
}
-
阅读以下关于某绘图系统的技术说明、部分UML类图及Visual Basic程序,将Visual Basic程序中(1)~(6)空缺处的语句填写完整。
【说明】
某绘图系统定义了一个抽象类Ishape,现有3个类Cpoint,CLine和Ccircle,它们都具有IShape界面。相应的类图关系如图5-11所示。

已知某第三方库已经提供了XCircle类,且完全满足CCircle图元显示时所需的功能。【Visual Basic代码6-1】是抽象类IShape类模块内容。【Visual Basic代码6-2】实现了类CCircle的IShape界面,并使用了XCircle提供的显示功能。
XCircle提供的显示功能方法接口为displayIt。
【Visual Basic代码6-1】
Publie Color As Long
Sub draw()
'方法体不包括可执行语句
End Sub
Sub move(stepx As Single, stepy As Single)
'方法体不包括可执行语句
End Sub
【Visual Basic代码6-2】
(1)
Private color As Long
… '其他定义省略
Private ridged As (2)
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
Set bridged=(3)
End Sub
Private Property (4) ()As Long
IShape_Color=color
End Property
Private Property (5) (ByVal newColor As Long)
Color=newColor
End Property
Private Sub IShape_draw() 使用XCircle提供的显示功能
(6)
End Sub
Private Sub IShape_move(stepx As Single, stepy As Single)
… '省略描述
End Sub
-
阅读以下应用程序说明和C程序,将C程序段中(1)~(7)空缺处的语句填写完整。
【说明】
某超市集团为发展业务向社会公开招聘N个工种的工作人员,每个工种各有不同的编号(1至M)和计划招聘人数。每位应聘者需申报两个工种,并参加集团组织的考试。该集团公司将按应聘者的成绩从高分至低分的顺序进行排队录取。具体录取原则是:从高分到低分依次对每位应聘者先按其第一志愿录取;当不能按其第一志愿录取时,便将他的成绩扣去5分后,重新排队,并按其第二志愿录取。
以下C程序为输出各工种实际招聘的应聘人员,每个工种都保留一个录取者的有序队列。录取处理循环直至招聘额满或已对全部应聘者都作了录取处理后跳出。
C程序中,类型STU包含有应聘者的基本信息:编号、成绩、志愿、排队成绩和录取志愿号。数组 rzl)的每个元素对应一个工种,包含有计划招聘人数和已录取的人数。
【C程序】
#include
#define N 36
#define EDMARK 5
typedef struct stu {
int no, total, z[2], sortm, zi;
struct stu *next;
} STU;
struct rznode {
int lmt, count;
STU *next;
} rz [N];
STU *head = NULL, *over = NULL;
int all
FILE *fp;
char dataf [ ] = "zp2008.dat" ;
print(STU *p)
{ for (;p!=NULL; p = p->next)
printf( "%d(%d) \t" , p->no, p->total
}
insert(STU **p, STU *u)
{ STU *v, *q;
for (q = *p;q != NULL; v = q , (1) )
if (q-> sortm < u->sortm)
break;
if ( q == *p)
(2);
else
(3);
u->next = q ;
}
main ( )
{ int zn, i, no, total, zl, z2 ;
STU *p, *v, *q;
fp = fopen(dataf, "r" );
if (fp == NULL)
{ printf ("Can't open file %s.kn" ,dataf);
exit (0);
}
fscanf (fp, "%d" ,&zn);
for (all = 0, i = 1; i <= zn; i++)
{ fscanf (fp, "%d", &rz [ i ].lmt ;
rz[i].count = 0;
rz[i].next = NULL;
all +=(4);
}
for (;;)
{ if (( fscanf(fp, "%d%d%d%d" ,&no,&total,&zl,&z2)) != 4 )
break;
p = ( STU *) malloc (sizeof (STU));
p->no = no;
p->total = p->sortm = total;
p->zi = 0;
p->z[0] = z1;
p->z[1] = z2;
(5);
}
fclose (fp);
for (;all && head != NULL;)
{ p = head;
head = head->next;
if (rz[p->z[p->zi]].count <(6))
{ rz[p->z[p->zi]].count ++;
insert(&rz[p->z[p->zi]].next,p);
all--;
continue;
}
if (p->zi >= 1 )
{ p->next = over;
ver = p;
continue;
}
p->sortm -= DEMARK;
(7);
insert(&head,p);
}
for (i = 1; i <= zn; i++ )
{ printf("%d:\n" ,i);
print( rz[i ].next);
printf(" \n");
}
printf( "over:\n" );
print(head);
print(over);
printf(" \n");
}
-
阅读以下应用程序说明和C程序,将C程序段中(1)~(7)空缺处的语句填写完整。
【说明】
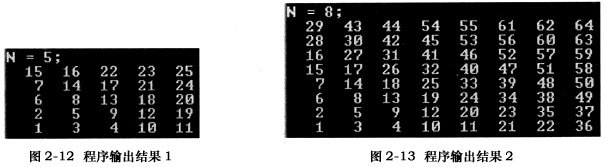
以下【C程序】能将自然数1,2,…,N2按蛇形方式逐个存入N阶矩阵。换言之,程序从anO开始到 aOn。为止(n=N-1)顺序填入自然数,交替地对每一斜列从左上元素向右下元素或从右下元素向左上元素存数。
例如,当N=5时,程序输出结果如图2-12所示;当N=8时,程序输出结果如图2-13所示。
【C程序】
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 10
int a[SIZE][SIZE], k;
main()
{ int i, j, n, N;
for (N = 3; N<=SIZE; N++)
{ k = 1;
makeArray (n = N-1);
printf ("\nN = %d;\n", n+1);
for (i = 0; i<=n; i++)
{ for (j = 0; j<=n; j++)
printf("%4d", a[i] [j]);
printf ("\n");
}
}
}
makeline (int row_start, int col_start, int row end)
{ /*完成矩阵一条斜线的整数填写*/
int i, j, sign =(1);
for (i = row_start, j = col start;(2); i += sign, j += sign)
a[i] [j] = k++;
}
makeArray (int n)
{ /*完成矩阵每条斜线的整数填写*/
int d;
for (d = 1; d <=(3); d++)
if (d <= n)
if (d%2)
makeline ((4));
else
makeline ((5));
else
if (d%2)
makeline ((6));
else
makeline ((7));
-
阅读以下函数说明和C程序,将C程序中(1)~(6)空缺处的语句补充完整。
【说明】
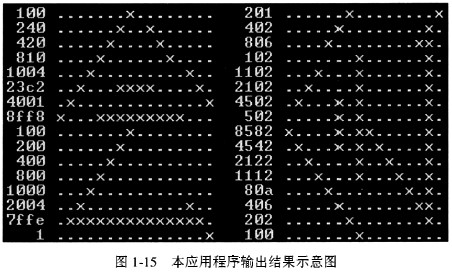
喜迎2008年北京奥运会!以下【C程序】能将一个给定汉字(例如,奥运会的“会”字)的点阵逆时针旋转90°,并输出旋转前后的点阵数据及字形。
图1-15是汉字“会”字的16×16点阵字形,用数字0表示空白位置,用数字1表示非空白位置,“会”字的第1行即可表示成如下的{0,1}序列:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
如果把它看做一个字的16个位,“会”字的第1行可以用十六进制数0100来表示。同理,“会”字的第2行可以用十六进制数0240表示,第3行可以用十六进制数0420表示……依此类推,用16个双字节整型数即可存放一个汉字点阵字形。“会”字的点阵数据及字形如图1-15的左半部分所示。
将一个汉字逆时针旋转90°,就是把该汉字点阵的最右列作为旋转后新点阵的第1行,次最右列作为旋转后新点阵的第2行……依此类推来形成一个旋转后的点阵字形。图1-15的右半部分就是将“会”字逆时针旋转90°后的点阵数据和字形(提示:读者可将书本顺时针旋转90°,以查看旋转90°后的点阵字形)。
在【C程序】中,数组old存放着“会”字的16个双字节整型点阵数据。函数turnleft能将该点阵数据逆时针旋转90°,旋转后的点阵数据存放在数组new中。函数display能将旋转前后的点阵数据加以编辑,用字符“.”表示值为0的位,用字符“x”表示值为1的位,从而将旋转前后的点阵按行输出其十六进制的数据和字形,如图1-15所示。
【C程序】
#include <stdio.h>
#define EMPTY '.'
#define NONEMPTY 'x'
#define LEFT 0
#define RIGHT 1
main ()
{ static unsigned old[16]=
{ 0x0100,0x0240,0x0420,0x0810,0x1004,0x23c2,
0x4001,0x8ff8,0x0100,0x0200,0x0400,0x0800,
0xl000,0x2004,0x7ffe,0x0001
};
unsigned new[16];
turnleft (old, new);
display (old,new);
}
turnleft (old,new)
unsigned old[],new[];
{ int row, k;
for (row=0;row<16;row++)
for ((1);k<16;k++)
new[row]|=((old[k]>>(2))&1) <<(3);
}
display (old, new)
unsigned *old,*new;
{ char out[2] [17],letter[2];
int row, col;
letter[O] = EMPTY;
letter[1] = NONEMPTY;
out[LEFT] [16]=out[RIGHT] [16]=(4);
for (row = 0;row<16;row++,old++,new++)
{ for (col = 0;co1<16;++col)
{ out[LEFT] [col] = letter[ ((5)) &1];
out[RIGHT] [col] = letter[ ((6)) &1];
}
printf("\n %4x %s",*old,&out[LEFT] [0]);
printf("%4x %s",*new,&out[RIGHT] [0]);
}
}
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟练习题之单选题(1
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(2)
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(3)
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟试题及答案
高级经济师考试试题及答案:单选练习题
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(2)




