阅读以下函数说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。
【函数2.1说明】
将一个正整数分解质因数。例如:输入90,打印出90=2*3*3*5。
【函数2.1】
Fun1 (int n)
{
int i;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
while ((1))
{
if (n%i==0)
{
printf("%d*",i);
(2);
}
else
break;
}
}
printf("%d",\n);
}
【函数2.2说明】
下面程序的功能是:海滩上有一堆桃子,5只猴子来分。第1只猴子把这堆桃子平均分为5份,多了一个,这只猴子把多的一个扔入海中,拿走了一份。第2只猴子把剩下的桃子又平均分成5份,又多了一个,它同样把多的一个扔入海中,拿走了一份。第 3、4、5只猴子都是这样做的,问海滩上原来最少有多少个猴子?
【函数2.2】
main()
{
int i,m,j,k,count;
for(i=4;i<10000;i+=4)
{
count=0;
(3);
for(k=0;k<5;k++)
{
(4);
i=j;
if(j%4==0)
(5);
else
break;
}
i=m;
if(count==4)
{
printf("%d\n",count);
break;
}
}
}
-
阅读以下说明和Java代码,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
主窗口有一个按钮、一个文本框和一个复选框,初始时窗口大小不能调整,选中复选框后窗口大小可以调整,如果撤销复选框的选择,则窗口的大小又不能调整,如下图所示。

【Java代码】
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
class MyFrame. extends Frame. implements ItemListener,ActionListener
{
Checkbox box;
TextArea text;
Button button;
MyFrame((1))
{
super(s);
box=new Checkbox("设置窗口是否可调整大小");
text=new TextArea(12,12);
button=(2) ("关闭窗口");
button.addActionListener(this);
box.addltemListener(this);
setBounds(100,100,200,300);
setVisible(true);
add(text,BorderLayout.CENTER);
add(box,BorderLayout.SOUTH);
add(button,BorderLayout.NORTH);
setResizable((3));
validate();
}
public void itemStateChanged(ItemEvent e)
{
if(box.getState()==true)
{
setResizable(true);
}
else
{
setResizable(false);
}
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
(4);
}
}
class simple
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
(5) ("simple");
}
}
-
阅读以下说明及C++程序代码,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
本程序的功能是生成螺旋方阵,用户可以输入该方阵的行列数,然后就生成对应的螺旋方阵。例如:当n=5时,对应的螺旋方阵如下:
1 16 15 14 13
2 17 24 23 12
3 18 25 22 11
4 19 20 21 10
5 6 7 8 9
【C++代码】
#include"stdio.h"
#include"iostream,h"
int array[11][11];
int temp;
int ROW;
void godown(int &m,int &a)
{
for(temp=1; temp<=ROW;temp++)
if(array[temp][a]==0)
array[temp][a]=(1);
a++;
}
void goright(int &m,int &b)
{
for(temp=1;temp<=ROW;temp++)
if(array[b][temp]==0)
array[b][temp]=m++;
b--;
}
void goup(int &m.int &c)
{
for(temp=ROW;temp>0;temp-)
if(array[temp][c]==0)
array[temp][c]=m++;
c--;
}
void goleft(int &m,int &d)
{
for(temp=ROW;temp>0;temp--)
if(array[d][temp]==0)
array[d][temp]=m++;
(2);
}
void main()
{
int a,b,c,d,max,m;
cin>>ROW;
cout>>end1;
for(a=1;a<=ROW;a++)
for(b=1;b<=ROW;b++)
(3);
m=1;
a=d=1;
b=c=ROW;
max=(4);
whiie(m<=max)
{
godown(m,a);
(5) (m,b);
goup(m,c);
goleft(m,d):
}
for(a=1;a<=ROW;a++)
{
for(b=1;b<=ROW;b++)
printf("%3d ",array[a][b]);
cout<<end1;
}
}
-
阅读以下说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
本程序从正文文件text.in中读入一篇英文短文,统计该短文中不同单词及出现次数,并按词典编辑顺序将单词及出现次数输出到正文文件word.out中。
程序用一棵有序二叉树存储这些单词及其出现的次数,边读入边建立,然后中序遍历该二叉树,将遍历经过的二叉树上的结点内容输出。
【函数】
# include <stdio.h>
# include <malloc.h>
# include <ctype.h>
# include <string.h>
# define INF "text.in"
# define OUTF "word.our'
typedef struct treenode {
char *word;
int count;
struct treenode *left, *right;
} BNODE;
int getword(FILE *fpt, char *word)
{ char c;
c=fgetc(tpt);
if (c==EOF)
return 0;
while(!(tolower(c)>= 'a' && tolower(c)<= 'z'))
{ c=fgetc(fpt);
if (c==EOF)
return 0;
} /* 跳过单词间的所有非字母字符 */
while(tolower(c)>= 'a' && tolower(c)<= 'z')
{ *word++=c;
c=fgetc(fpt);
}
*word='\0';
return 1;
}
void binary_tree(BNODE **t, char *word)
{ BNODE *ptr, *p; int compres;
p=NULL;
(1);
while (ptr) /* 寻找插入位置 */
{ compres=strcmp(word, ptr->word);/* 保存当前比较结果 */
if (!compres)
{ (2); return;}
else
{ p=ptr;
ptr=compres>0 ? ptr->right: ptr->left;
}
}
ptr=(BNODE *)malloc(sizeof(BNODE));
ptr->left=ptr->right=NULL;
ptr->word=(char *)malloc(strlen(word)+1);
strcpy(ptr->word, word);
(3);
if (p==NULL)
*t=ptr;
else if (compres>0)
p->right=ptr;
else
p->left=ptr;
}
void midorder(FILE *fpt, BNODE *t)
{ if (t==NULL)
return;
midorder(fpt,(4));
fprintf(fpt, "%s %d\n", t->word, t->count);
midorder(fpt, t->right);
}
void main()
{ FILE *fpt; char word[40];
BNODE *root=NULL;
if ((fpt=fopen(INF, "r"))==NULL)
{ printf("Can't open file %s\n", INF);
return;
}
while(getword(fpt, word)==1)
binary_tree((5));
fclose(fpt);
fpt=fopen(OUTF, "w");
if (fpt==NULL)
{ printf("Can't open fife %s\n", OUTF);
return;
}
midorder(fpt, root);
fclose(fpt);
}
-
阅读以下说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
下面的程序构造一棵以二叉链表为存储结构的二叉树。
【函数】
BitTree *createbt(BitTree *bt)
{
BitTree *q;
struct node *s[30];
int j,i;
char x;
printf("i,x=");
scant("%d,%c",&i,&x);
while(i!=0 && x!='$')
{
q=(BitTree *}malloc(sizeof(BitTree));//生成一个结点
(1);
q->lchild=NULL;
q->rchild=NULL;
(2) ;
if ((3))
{
j=i/2; // j为i的双亲结点
if(i%2==0)
(4); //i为j的左孩子
else
(5); //i为j的右孩子
}
printf("i,x=");
scanf("%d,%c",&i,&x);
}
return s[i];
}
-
阅读以下函数说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。
【函数2.1说明】
将一个正整数分解质因数。例如:输入90,打印出90=2*3*3*5。
【函数2.1】
Fun1 (int n)
{
int i;
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
while ((1))
{
if (n%i==0)
{
printf("%d*",i);
(2);
}
else
break;
}
}
printf("%d",\n);
}
【函数2.2说明】
下面程序的功能是:海滩上有一堆桃子,5只猴子来分。第1只猴子把这堆桃子平均分为5份,多了一个,这只猴子把多的一个扔入海中,拿走了一份。第2只猴子把剩下的桃子又平均分成5份,又多了一个,它同样把多的一个扔入海中,拿走了一份。第 3、4、5只猴子都是这样做的,问海滩上原来最少有多少个猴子?
【函数2.2】
main()
{
int i,m,j,k,count;
for(i=4;i<10000;i+=4)
{
count=0;
(3);
for(k=0;k<5;k++)
{
(4);
i=j;
if(j%4==0)
(5);
else
break;
}
i=m;
if(count==4)
{
printf("%d\n",count);
break;
}
}
}
-
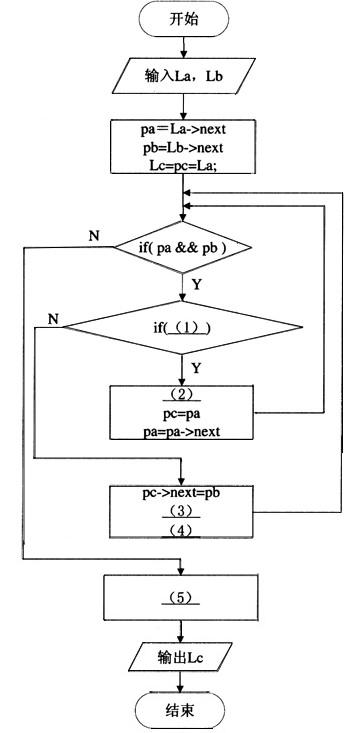
阅读以下说明和流程图,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
已知头指针分别为La和lb的有序单链表,其数据元素都是按值非递减排列。现要归并La和Lb得到单链表Lc,使得Lc中的元素按值非递减排列。程序流程图如下所示:
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟练习题之单选题(1
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(2)
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(3)
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟试题及答案
高级经济师考试试题及答案:单选练习题
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(2)

