阅读以下说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
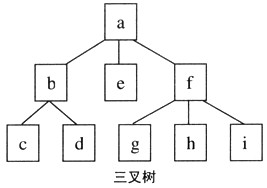
设M叉树采用列表法表示,即每棵子树对应一个列表,列表的结构为:子树根结点的值后跟用“()”括起来的各子树的列表(若有子树的话),各子树的列表间用“,”分隔。例如,如下图所示的三叉树可用列表a(b(c,d),e,f(g,h,i))表示。
本程序根据输入的列表生成一棵M叉树,并由M叉树再输出列表。
【函数】
#include
#include
#define M 3 /*三叉树*/
typedef struct node{
int val;
struct node *subTree[M];
}NODE;
char buf[255], *str=buf;
NODE *d=NULL;
NODE *makeTree() /*由列表生成M叉树*/
{
int k; NODE *s;
s=(1);
s->val=*str++;
for(k=0;k<M;k++)
s->subTree[k]=NULL;
if(*str=='(')
{
k=0;
do{
str++;
s->subTree[k]=(2);
if(*str==')')
{
str++;
break;
}
k=k+1;
}while((3));
}
return s;
}
void walkTree(NODE *t) /*由M叉树输出列表*/
{
int i;
if(t !=NULL)
{
(4);
if(t->subTree[0]==NULL)
return;
putchar('(');
for(i=0;i<M;i++)
{
(5);
if(i !=M-1 && t->subTree[i+1]!=NULL)
putchar(',');
}
putchar(')');
}
}
void main()
{
printf("Enter exp: ");
scanf("%s",str);
d=makeTree();
walkTree(d);
putchar('\n');
}
-
阅读以下说明,以及用C++在开发过程中所编写的程序代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
在下面函数横线处填上适当的字句,使其输出结果为:
构造函数.
构造函数.
1,2
5,6
析构函数
析构函数.
【C++代码】
#include "iostream.h"
class AA
{ public;
AA(int i,int j)
{A=i; B=j;
cout<<"构造函数.\n";
}
~AA(){(1);}
void print();
private:
int A, B;
};
void AA∷print()
{cout<<A<<","<<B<<endl;}
void main()
{
AA *a1, *a2;
(2)=new AA(1, 2);
a2=new AA(5, 6);
(3);
a2->print();
(4) a1;
(5) a2;
}
-
阅读以下说明和Java代码,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
下面程序完成从键盘读入一个字符串,然后采用parseInt方法将其转换为一个相应的整数。
import java.io.*;
public class testThrows{
public static (1) readString() (2) IOException{
int ch;
String r="";
boolean done=false;
while((3)){
ch=System.in.read();
if(ch<0 || ch=0xd) //处理回车符中第一个符号
done=true;
else
r=r+(char)ch;
}
return r;
}
public static void main(Stling args[]){
String str;
(4) {
str=readString();
} (5) (IOException e){
System.out.println("error");
return;
}
System.out.println("input integer: "+Integer.parselnt(str));
}
}
-
阅读以下说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
本程序利用非递归算法实现二叉树后序遍历。
【函数】
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct node{/*二叉树的结点数据结构类型*/
char data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
}BTREE;
void SortTreelnsert(BTREE **tree, BTREE *s)
{
if(*tree==NULL)*tree=s;
else
if(s->data<(*tree)->data)
SortTreelnsert((1),s);
else if(s->data>=(*tree)->data)
SortTreelnsert((2),s);
}
void TraversalTree(BTREE *tree)
{
BTREE *stack[1 000],*p;
int tag[1000],top=0;
p=tree;
do{
while(p !=NULL)
{
stack[++top]=p;
(3);
tag[top]=0; /*标记栈顶结点的左子树已进行过后序遍历*/
}
while(top>0&&(4))/*栈顶结点的右子树是否被后序遍历过*/
{
p=stack[top--];
putchar(p->data);
}
if(top>0)/*对栈顶结点的右子树进行后序遍历*/
{
(5);
tag[top]=1;
}
}while(top>0);
}
void PrintSortTree(BTREE *tree)
{
if(tree !=NULL)
{
printSortTree(tree->left);
putchar(tree->data);
pdntSortTree(tree->right);
}
}
main()
{
BTREE *root=NULL, *node;
char ch;
ch=getchar();
while(ch !='#')
{
node=(BTREE*)malloc(sizeof(BTREE));
node->data=ch;
node->left=node->right=NULL;
SortTreelnsert(&root, node);
ch=getchar();
}
PrintSortTree(root);
putchar('\n');
TraversalTree(root);
}
-
阅读以下说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
设M叉树采用列表法表示,即每棵子树对应一个列表,列表的结构为:子树根结点的值后跟用“()”括起来的各子树的列表(若有子树的话),各子树的列表间用“,”分隔。例如,如下图所示的三叉树可用列表a(b(c,d),e,f(g,h,i))表示。
本程序根据输入的列表生成一棵M叉树,并由M叉树再输出列表。

【函数】
#include
#include
#define M 3 /*三叉树*/
typedef struct node{
int val;
struct node *subTree[M];
}NODE;
char buf[255], *str=buf;
NODE *d=NULL;
NODE *makeTree() /*由列表生成M叉树*/
{
int k; NODE *s;
s=(1);
s->val=*str++;
for(k=0;k<M;k++)
s->subTree[k]=NULL;
if(*str=='(')
{
k=0;
do{
str++;
s->subTree[k]=(2);
if(*str==')')
{
str++;
break;
}
k=k+1;
}while((3));
}
return s;
}
void walkTree(NODE *t) /*由M叉树输出列表*/
{
int i;
if(t !=NULL)
{
(4);
if(t->subTree[0]==NULL)
return;
putchar('(');
for(i=0;i<M;i++)
{
(5);
if(i !=M-1 && t->subTree[i+1]!=NULL)
putchar(',');
}
putchar(')');
}
}
void main()
{
printf("Enter exp: ");
scanf("%s",str);
d=makeTree();
walkTree(d);
putchar('\n');
}
-
阅读以下函数说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。
【函数1.1说明】
本程序可以打印出如下图形(菱形):
*
***
*****
*******
*****
***
*
【函数2.1】
main()
{
int i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<=3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<=2-i;j++)
printf(" ");
for((1))
printf("*");
printf("\n");
}
for(i=0;i<=2;i++)
{
for((2))
printf(" ");
for(k=0;k<=4-2*i;k++)
printf("*");
printf("\n");
}
}
【函数2.2说明】
通过本程序,可以从键盘输入一个字符串,将小写字母全部转换成大写字母,然后输出到一个磁盘文件“CsaiWgm”中保存,输入的字符串以“!”结束。
【函数2.2】
#include "stdio.h"
main()
{
FILE *fp;
char str[100],filename[10];
int i=0;
if((fp=fopen("CsaiWgm","w"))==NULL)
{
printf("cannot open the file\n");
exit(0);
}
printf("please input a string:\n");
gets(str);
while((3))
{
if(str[i]>='a'&&str[i]<='z')
str[i]=(4);
fputc(str[i],fp);
(5);
}
fclose(fp);
fp=fopen("CsaiWgm","r");
fgets(str,stden(str)+1,fp);
printf("%s\n",str);
fclose(fp);
}
-
阅读下列算法说明和代码,将应填入(n)处的语句写在对应栏内。
【说明】
本程序用古典Eratosthenes;筛选法求从2起到指定范围内的素数。如果要找出2~10中的素数,开始时筛中有2~10的数,然后取走筛中最小的数2,宣布它是素数,并把该素数的倍数都取走。这样,第一步以后,筛子中还留下奇数3、5、7、9;重复上述步骤,再取走最小数3,宣布它为素数,并取走3的倍数,于是留下5、7。反复重复上述步骤,直到筛中为空时,工作结束,求得2~10中的全部素数。
【代码】
# include <stdio.h>
# define MAX 22500
/*程序中用数组sieve表示筛子,数组元素sieve[i]的值为1时,表示数i在筛子中,值为-1时表示数i已被取走*/
main()
{ unsigned int i, range, factor, k;
int sieve[MAX];
printf("please input the range:");
scanf("%d", &range);/* range 指出在多大的范围内寻找素数*/
for(i=2; i<=range; i++)
(1);
factor=2;
while (factor<=range)
{ if((2)) /* 筛中最小数是素数 */
{ printf("%d\t", factor);
k=factor;
while (k<=range) /*移走素数的倍数 */
{ (3);
k=(4);
}
}
(5);
}
}
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟练习题之单选题(1
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(2)
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(3)
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟试题及答案
高级经济师考试试题及答案:单选练习题
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(2)