阅读以下函数说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。
[说明1]
函数void fun(char*w,char x,int*n)用来在w数组中插入x,w数组中的数已按由小到大顺序存放,n指存储单元中存放数组中数据的个数,插入后数组中的数仍有序。
[C函数1]
void fun(char*W,char x,int*n)
{ int i,P;
p=0;
w[*n]=x;
while(x>w[p]) (1) ;
for(i=*n,i>p;i--)w[i]=(2);
w[p]=x;
++*n;
}
[说明2]
函数void revstr(char*s)将字符串s逆置。例如:字符串“abcde”,经过逆置后变为“edcba”。
[C函数2]
void revstr(char*s)
{ char*p,c;
if(s==NULL)return;
p=(3); /*p指向字符串s的最后一个有效字符*/
while(s<p){ /*交换并移动指针*/
C=*s;
(4)=*p;
(5)=c;
}
}
-
阅读以下说明和Java代码,将解答写在对应栏内。
[说明]
已知类Stock和类JavaMain都定义在JavaMain.java文件中,类stock的定义中有四处错误,分别在代码的第01、02、06、07行。请修改错误并给出修改后该行的完整代码,并写出改正错误后程序运行的输出结果。
[Java代码]
01 public class Stock{
02 static {
03 shares=0;
04 Share_val=0.0;
05 }
06 private Stock()tgetData();}
07 private Stock(int n,double pr=0){
08 shares=n;
09 share val=pr;
10 getData();
11 }
12 public void getData(){
13 System.out.print(shares+":"+share_val+" ");
14 }
15 Drivate int shares; //非静态变量
16 Drivate double share val; //非静态变量
17 };
18
19 publiC class JavaMain{
20 public static void main(String args[]){
21 Stock a=new Stock();
22 Stock b=new Stock(1,67.5);
23 //其他代码省略,且代码无输出
24 }
25 }
-
阅读以下说明和C++程序,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。
[说明]
下面程序输出一个矩形面积,以及矩形区域上的假想的作物产量。
[C++程序]
#include <iostream.h>
class crop_assessment
{
int actual_crop;
int ideal_crop;
public:
void set(int in_actual,int in_ideal)
{
actual crop=in_actual;
ideal_crop=in_ideal;
}
int get_actual_crop(void){ (1) ;}
int get_ideal_crop(void){ (2) ;)
};
Class lot_size
{
int length;
int width;
(3) crop;
public:
void set(int 1,int w,int a,int i)
{
length=1;
width=w;
crop.set(a,i);
}
int get_area(void){return length*width;}
int get_data(void){return (4) ;}
int get_data2(void)freturn (5) ;}
}
int main()
{
Los_size small,medium;
small.set(5,5,5,25);
medium.set(10,10,10,50);
cout<<"For a small lot of area"<<smallget_area()<<“\n”;
cout<<"the actual crops are$"<<small.get_data2()<<"\n";
cout<<"and ideal crops are$”<<small.get_data()<<"\n";
cout<<"For a medium Lot of area"<<medium.get area()<<:\n”;
cout<<"the actual crops are$"<<medium.get_data2()<<"\n";
cout<<"and ideal crops are$"<<medium.get_data()<<"\n";
return 0;
}
-
阅读以下函数说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。
[说明]
本程序实现对指定文件内的单词进行计数。其中使用二叉树结构来保存已经读入的不同单词,并对相同单词出现的次数进行计数。此二叉树的左孩子结点的字符串值小于父结点的字符串值,右孩子结点的字符串值大于父结点的字符串值。函数getword(char*filename,char*word)是从指定的文件中得到单词。char*strdup(char*S)是复制S所指向的字符串,并返回复制字符串的地址。
[C程序]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXWORD 100
struct node {
char*word;
int count;
struct node*left;
struct node*right;
}
struct node*addtree(struct node*P,char*w)
{ int cond;
if(p==NULL){ /*向树中插入结点*/
P=(struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
P->word=strdup(w);
P->count=1;
(1) ;
}
elseif((oond=strcmp(w,p->word))==0) (2) ;
else if(cond<0)p->left=(3);
else p->right=(4);
return p;
}
main()
{ Struct node*root;
char word[MAXWORD];
root=NULL;
filename="example.dat";
while(getword(filename,word)!=EOF))
root=(5);
}
-
阅读以下函数说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。
[说明]
已知r[1...n]是n个记录的递增有序表,用折半查找法查找关键字为k的记录。若查找失败,则输出“failure",函数返回值为0;否则输出“success”,函数返回值为该记录的序号值。
[C函数]
int binary search(struct recordtype r[],int n,keytype k)
{ intmid,low=1,hig=n;
while(low<=hig){
mid=(1);
if(k<r[mid].key) (2);
else if(k==r[mid].key){
printf("succesS\n");
(3);
}
else (4);
}
printf("failure\n");
(5);
}
-
阅读以下函数说明和C语言函数,将应填入(n)处的字句写在对应栏内。
[说明1]
函数void fun(char*w,char x,int*n)用来在w数组中插入x,w数组中的数已按由小到大顺序存放,n指存储单元中存放数组中数据的个数,插入后数组中的数仍有序。
[C函数1]
void fun(char*W,char x,int*n)
{ int i,P;
p=0;
w[*n]=x;
while(x>w[p]) (1) ;
for(i=*n,i>p;i--)w[i]=(2);
w[p]=x;
++*n;
}
[说明2]
函数void revstr(char*s)将字符串s逆置。例如:字符串“abcde”,经过逆置后变为“edcba”。
[C函数2]
void revstr(char*s)
{ char*p,c;
if(s==NULL)return;
p=(3); /*p指向字符串s的最后一个有效字符*/
while(s<p){ /*交换并移动指针*/
C=*s;
(4)=*p;
(5)=c;
}
}
-
阅读以下说明和流程图,回答问题将解答填入对应栏。
[说明]
下面的流程图,用来完成计算一组数组中的中值,其方法是:将数组中的一个值与其他值比较,并计算大于等于被比较数的数值的个数,以及小于等于被比较数的数值的个数,如果两数都大于n/2,则已经找到了中值,否则继续之前的步骤。
注:流程中循环开始的说明按照“循环变量:循环初值,循环终值,增量”格式描述;
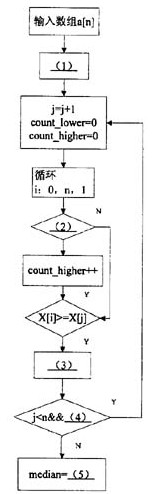
[问题]
将流程图的(1)~(5)处补充完整。
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟练习题之单选题(1
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(2)
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(3)
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟试题及答案
高级经济师考试试题及答案:单选练习题
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(2)
