You are the administrator of a SQL Server 2000 computer. The server contains a database named Inventory. The Inventory database has a table named StorageLocations that stores the location of parts contained in your company's warehouses. The StorageLocations table is configured as shown in the exhibit.

The LocationDescription field is usually described with a name 10 to 25 characters in length. The locations never store more than 100,000 units of any given part.
You want to modify the table's schema to save space. You cannot lose any existing data. You want to do this by using the minimum amount of administrative time and server resources.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you execute?
- A.ALTER TABLE [dbo].[StorageLocations] ALTER COLUMN [UnitsStored] [int] NOT NULL
- B.ALTER TABLE [dbo].[StorageLocations] [LocationDescription] [char] (25) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NOT NULL
- C.ALTER TABLE [dbo].[StorageLocations] ALTER COLUMN [UnitsStored] [smallint] NOT NULL
- D.ALTER TABLE [dbo].[StorageLocations] [LocationDescription] [nvarchar] (25) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NOT NULL
-
You are the administrator of SQL Server 2000 computer. The server contains a database named Medical Records. This database contains clinical records and administrative records. The database consumes about 30GB of disk space. The data files are configured as shown in the exhibit.
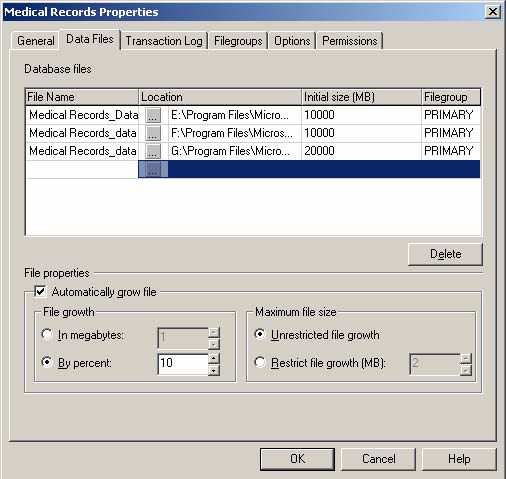
You run full database backups each night after business hours. You notice that the backup is not complete by the time the morning shift begins to use the database.
You need to minimize the time needed to restore data in the event of a system, failure. You also want to reconfigure the database to allow the backups to complete during the evening hours.
Which two actions should you take? (Each correct answer represents part of the solution. Choose two)
A. Reorganize the data files into two groups. Place the system tables in the PRIMARY filegroup and the user-defined tables in the other filegroup.
B. Reorganize the data files into three groups. Place the system tables and shared objects in the PRIMARY filegroup, the clinical records in a filegroup, and the administrative records in a filegroup.
C. Reorganize the data files into three groups. Place the system tables in the PRIMARY filegroup, the indexes in a filegroup, and the tables in the other filegroup.
D. Back up the transaction log each night. Run a filegroup backup on a different filegroup each night.
E. Back up the transaction log each night. Run a filegroup backup on the database each weekend.
F. Back up the transaction log each night. Run a differential backup each Sunday, and run a full backup the first day of each month.
-
You are the administrator of a SQL Server 2000 computer. The server contains a Data Transformation Services (DTS) package that queries multiple databases and writes the results to a text file. You run this package by using a Microsoft Windows batch file. The batch file uses the dtsrun utility to execute the DTS package.
You want to ensure that connection properties, such as login names and passwords, cannot be read or modified by users. Which two actions should you take? (Each correct answer represents part of the solution. Choose two.)
- A.Save the DTS package so that it has an owner password.
- B.Save the DTS package so that it has a user password.
- C.Encrypt the DTS package details in the command line of the dtsrun utility.
- D.Store the DTS package in the Meta. Data Services repository.
- E.Store the DTS package as a Microsoft Visual Basic file.
-
You are the administrator of several SQL Server 2000 computers. A data Transformation Services (DTS) package uses native OLE DB providers to transfer data between the servers. Connection details for the servers are specified in .udl files. The .udl files are frequently updated as connection details change.
You want to distribute the DTS package as a file to developers in your company. You want to make sure connection details are available to developers who receive the DTS package.
Which two tasks should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two)
- A.Enable the Always read properties from UDL file option in the Connection Properties dialog box.
- B.Disable the Always read properties from UDL file option in the Connection Properties dialog box.
- C.Delete the .udl files and store connection details in the registry by using system data source names.
- D.Delete the .udl files, and store connection details in the registry by using user data source names.
- E.Make the .udl files available on a network share.
-
You are the administrator of SQL Server computers. One server is named SQL7, and other is named SQL2000. SQL7 is running SQL Server 7.O and SQL2000 is running SQL Server 2000.
The net-libraries on SQL2000 are configured as shown in the exhibit.
SQL7 is configured so that it has the named pipes, TCP/IP, NWlink, IPX/SPX and multiprotocol Net Libraries.
SQL2000 and SQL7 exchange confidential company information. You need to ensure that unauthorized users cannot access this information.
Which two actions should you take? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two)
- A.On SQL2000, enable the multiprotocol net library.
- B.On SQL2000, select the force protocol encryption check box.
- C.On SQL7, select the force protocol encryption check box.
- D.On SQL2000, install a secure sockets layer (SSL) encryption certificate.
- E.On SQL2000 and SQL7, enable multiprotocol encryption.
-
You are the administrator of a SQL Server 2000 computer. The server contains a database named Customers, which is used by a custom client/server application.
The database contains more than 1 million rows. Users report that the database responds slowly when they search for customers by using the application. Users search for customers by scrolling through an alphabetical list of customer names.
You use SQL profiles to capture information about how the application uses the database.
You receive results as shown in the following screen shot.

You need to improve the application’s performance. What should you do?
- A.Create additional nonclustered indexes on the CustomerInformation table.
- B.Rewrite the application so that it uses a user-defined function to return the customer list.
- C.Rewrite the application so that it uses a query with a WHERE clause to search for customer names.
- D.Rewrite the application so that is uses a stored procedure to return the customer list.
-
You are the administrator of a SQL Server 2000 computer. The server contains a database named Contracts. The server is configured as shown in the server configuration exhibit.

The database files are configured as shown in the database properties exhibit.

The database developers have been creating new tables and indexes without specifying a filegroup.
The primary filegroup is reaching its maximum capacity.
You want the developers to continue adding new objects, but you do not want then to change the way they create objects. You do not want to run out of disk space. You also want to minimize the time it takes to administer the database.
What should you do?
- A.Back up the existing objects on the PRIMARY filegroup. Drop them from the database. Re-create them on the SECONDARY filegroup.
- B.Set the file growth on the PRIMARY filegroup to UNLIMITED.
- C.Set the PRIMARY filegroup so that it is read-only.
- D.Set the SECONDARY filegroup as the default filegroup.
-
You are the administrator of a SQL Server 2000 computer. The server contains a database named sales. You need to change the way customer Ids appear in the Customers table. The database schema is shown in the exhibit.

You need to automate the process of updating the primary key tools. You also want to minimize records locks and administration within the database during the update process.
What should you do?
- A.Add an ON UPDATE CASCADE constraint to the CustomerID field in the Customers table. Modify the values in the CustomerID field in the Customers table.
- B.Create a duplicate record that has a new CustomerID value. Update the foreign key fields in the invoices, contacts, and quotes tables with the new value.
- C.Disable the FOREIGN KEY constraints. Within a transaction, modify the values in the CustomerID field in the Customers table and all related foreign key values in the invoices, contacts, and quotes tables. Re-enable the FOREIGN KEY constraints after the
- D.Create a Data Transformation Services package. Use the package to transform. the CustomerID value and the values of the related foreign keys in the invoices, contacts, and quotes tables.
-
You are the database administrator for a financial services company. Employees enter data 24 hours a day into a SQL Server 2000 database. These employees report slower response times when new account information is gathered from branch offices and added to the database. You currently use the following BULK INSERT statement to add the account information:
BULK INSERT finance.dbo.customers
FROM ‘di\bulk\accts143_10141000.txt’
WITH DATAFILETYPE = ‘char’,
FIELD/TERMINATOR = ‘\t’,
ROWTERMINATOR = ‘\n,’
TABLOCK
You want to ensure that response times do not slow when new account information is added to the database. What should you do?
- A.Drop the indexes for the customers table before the data load, and then re-create the indexes after the data load is complete.
- B.Remove the TABLOCK option from the BULK INSERT statement.
- C.Add the BATCHSIZE option to the BULK INSERT statement and then set the option equal to 10 percent of the number of rows to be loaded.
- D.Add the ROWS_PER_BATCH option to the BULK INSERT statement and then set the option equal to 10 percent of the number of rows to be loaded.
-
You are the database administrator for a retail company. The company owns 270 stores. Every month, each store submits approximately 2,000 sales records, which are loaded into a SQL Server 2000 database at the corporate headquarters.
- A Data Transformation Services (DTS) package transforms the sales records, as they are loaded. The package writes the transformed sales records to the Sales table, which has a column for integer primary key values. The IDENTITY property automatically assi
- After loading this month's sales data, you discover that a portion of the data contains errors. You stop loading data, identify the problem records, and delete those records from the database. You want to reuse the key values that w
- A.Export all records from the Sales table to a temporary table. Truncate the Sales table, and then reload the records from the temporary table.
- B.Export all records from the Sales table to a text file. Drop the Sales table, and then reload the records from the text file.
- C.Use the DBCC CHECKIDENT statement to reseed the Sales table's IDENTITY property.
- D.Set the Sales table's IDENTITY_INSERT property to ON. Add new sales records that have the desired key values.
-
You are the administrator of a SQL Server 2000 computer. The server contains a database named Inventory. The Inventory database has a table named StorageLocations that stores the location of parts contained in your company's warehouses. The StorageLocations table is configured as shown in the exhibit.

The LocationDescription field is usually described with a name 10 to 25 characters in length. The locations never store more than 100,000 units of any given part.
You want to modify the table's schema to save space. You cannot lose any existing data. You want to do this by using the minimum amount of administrative time and server resources.
Which Transact-SQL statement should you execute?
- A.ALTER TABLE [dbo].[StorageLocations] ALTER COLUMN [UnitsStored] [int] NOT NULL
- B.ALTER TABLE [dbo].[StorageLocations] [LocationDescription] [char] (25) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NOT NULL
- C.ALTER TABLE [dbo].[StorageLocations] ALTER COLUMN [UnitsStored] [smallint] NOT NULL
- D.ALTER TABLE [dbo].[StorageLocations] [LocationDescription] [nvarchar] (25) COLLATE SQL_Latin1_General_CP1_CI_AS NOT NULL
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟练习题之单选题(1
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(2)
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(3)
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟试题及答案
高级经济师考试试题及答案:单选练习题
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(2)




