阅读下列说明和C函数,填补C函数中的空缺,将解答填入答案纸的对应栏目内。
【说明】
字符串是程序中常见的一种处理对象,在字符串中进行子串的定位、插入和删除是常见的运算。
设存储字符串时不设置结束标志,而是另行说明串的长度,因此串类型定义如下:
typedef struct ﹛
Char *str; //字符串存储空间的起始地址
int length; //字符串长
int capacity; //存储空间的容量
﹜SString;
【函数1说明】
函数indexStr(S,T,pos)的功能是:在S 所表示的字符串中,从下标pos开始查找T所表示字符串首次出现的位置。方法是:第一趟从S中下标为pos、T中下标伟0的字符开始,从左往右逐个对于来比较S和T的字符,直到遇到不同的字符或者到达T的末尾。若到达T的末尾,则本趟匹配的起始下标pos为T出现的位置,结束查找;若遇到了不同的字符,则本趟匹配失效。下一趟从S中下标pos+1处的字符开始,重复以上过程。若在S中找到T,则返回其首次出现的位置,否则返回-1。
例如,若S中的字符为伟”students ents”,T中的字符串伟”ent",pos=0,则T在S中首次出现的位置为4。
【C函数1】
int index Str(SString S ,SString T,int pos)
﹛
int i,j:
i (S.length<1||T.length<1||pos+T.length-1)
return-1;
for(i=pos,j=0;i if (S.str[i]==T.str[j])﹛ i++;j++; ﹜ else﹛ i=( 1 );j=0 ﹜ ﹜ if ( 2 )return i -T.length; return-1; ﹜ 【函数2说明】 函数 eraseStr(S,T}的功能是删除字符串S中所有与T相同的子串,其处理过程为: 首先从字符串 S 的第一个字符(下标为0)开始查找子串T,若找到〈得到子串在S中的起始位置),则将串 S 中子串T之后的所有字符向前移动,将子串T覆盖,从而将其删除,然后重新开始查找下一个子串T,若找到就用后面的宇符序列进行覆盖,重复上述过程,直到将S中所有的子串T删除。 例如,若字符串 S为 “12ab345abab678”、T为“ab”。第一次找到“ab”时(位置为2),将“345abab678”前移,S 中的串改为“12345abab678” ,第二次找到“ab”时(位置为 5);将“ab678”前移,S中的串改为“12345ab678”,第三次找到“ab”时(位置为5);将“678”前移 ,S中的串改为“12345678 ”。 【C函数2】 Void eraseStr(SString*S,SStringT) ﹛ int i; int pos; if (S->length<1||T.length<1||S->length return; Pos=0; for(;;)﹛ //调用indexStr在S所表示串的pos开始查找T的位置 Pos=indexStr( 3 ); if(pos=-1) //S所表示串中不存在子串T return; for(i=pos+T.length;i S->str[( 4 )]=S->str[i]; S->length=( 5 ); //更新S所表示串的长度 ﹜ ﹜
-
阅读以下说明和 Java程序,填补代码中的空缺,将解答填入答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
以下Java代码实现一个简单客户关系管理系统(CRM)中通过工厂(CustomerFactory )对象来创建客户(Customer)对象的功能。客户分为创建成功的客户(RealCustomer)和空客户 (NullCustomer)。空客户对象是当不满足特定条件时创建或获取的对象。类间关系如图 5-1 所示。
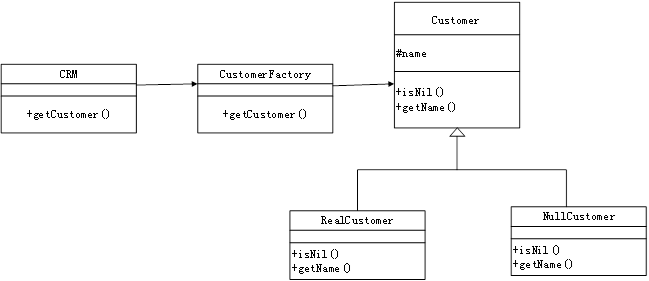
图5-1 类图
【Java代码】
Abstract class Customer﹛
Protected String name;
( 1 )boolean isNil();
( 2 )String getName();
﹜
Class RealCustomer( 3 )Customer{
Public RealCustomer(String name){ this.name=name; }
Public String getName(){ return name ; }
Public boolean is Nil() { return false; }
﹜
Class NullCustomer( 4 )Customer﹛
Public String getName()﹛ return "Not Available in Customer Database"; ﹜
Public boolean isNil() ﹛ return true; ﹜
﹜
class Customerfactory {
public String[] names = {"Rob","Joe","Julie"};
public Customer getCustomer(String name) {
for (int i = 0; i< names.length;i++) {
if (names[i].( 5 ))﹛
return new RealCustomer(name);
﹜
﹜
return( 6 );
﹜
﹜
Public class CrM﹛
Public viod get Customer()﹛
Customerfactory( 7 );
Customer customer1-cf.getCustomer("Rob");
Customer customer2=cf.getCustomer("Bob");
Customer customer3= cf.getCustomer("Julie");
Customer customer4= cf.getCustomer("Laura");
System.out.println("customers”)
System.out.println(customer1.getName());
System.out.println(customer2getName());
System.out.println(customer3.getName());
System.out.println(customer4.getName());
﹜
Public static viod main (String[]arge)﹛
CRM crm =new CRM();
Crm.getCustomer();
﹜
﹜
/*程序输出为:
Customers
rob
Not Available in Customer Database
Julie
Not Available in Customer Database
*/
-
阅读下列说明和C++代码,填补代码中的空缺,将解答填入答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
以下C++代码实现一个简单客户关系管理系统(CrM)中通过工厂(Customerfactory)对象来创建客户(Customer)对象的功能。客户分为创建成功的客户(realCustomer)和空客户(NullCustomer)。空客户对象是当不满足特定条件时创建或获取的对象。类间关系如图6-1所示。
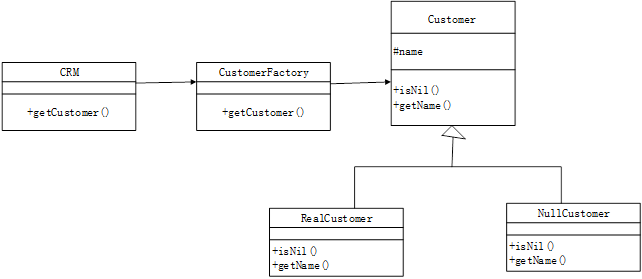
图6-1
【C++代码】
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class Customer{
protected:
string name;
public:
( 1 ) boll isNil()=0;
( 2 ) string getName()=0;
﹜;
class RealCustomer ( 3 ){
Public:
realCustomer(string name){this->name=name;﹜
bool isNil(){ return false; ﹜
string getName(){ return name; ﹜
﹜;
class NullCustomer ( 4 ) {
public:
bool isNil(){ return true; ﹜
string getName(){ return 〝Not Available in Customer Database〞; ﹜
﹜;
class Customerfactory{
public:
string names[3]={〝rob〞, 〝Joe〞,〝Julie〞﹜;
public:
Customer*getCustomer(string name){
for (int i=0;i<3;i++){
if (names[i].( 5 ) ){
return new realCustomer(name);
﹜
﹜
return( 6 );
﹜
﹜;
class CRM{
public:
void getCustomer(){
Customerfactory*( 7 );
Customer*customer1=cf->getCustomer(〝Rob〞);
Customer*customer2=cf->getCustomer(〝Bob〞);
Customer*customer3=cf->getCustomer(〝Julie〞);
Customer*customer4=cf->getCustomer(〝Laura〞);
cout<<〝Customers〞<
cout<
getName()< cout<
getName()< cout<
getName()< cout<
getName()< delete cf;
﹜
﹜;
int main(){
CRM*crs=new CRM();
crs->getCustomer();
delete crs;
return 0;
﹜
/*程序输出为:
Customers
rob
Not Available in Customer Database
Julie
Not Available in Customer Database
*/
-
阅读以下说明和C 函数,填补函数中的空缺,将解答填入答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
简单队列是符合先进先出规则的数据结构,下面用不含有头结点的单向循环链表表示简单队列。
函数EnQueue(Queue *Q,KeyType new_elem) 的功能是将元素new_elem加入队尾。
函数DnQueue(Queue *Q,KeyType *elem)的功能使将非空队列的队头元素出队(从队列中删除),并通过参数带回刚出队的元素。
用单向循环链表表示的队列如图 4-1 所示。
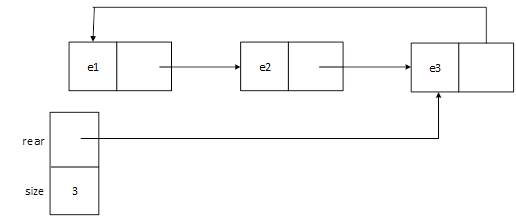
图4-1 单向循环链表表示的队列示意图
队列及链表结点等相关类型定义如下:
enum {ERROR, OK};
typedef int KeyType;
typedef struct QNode﹛
KeyType data;
Struct QNode*next;
﹜QNode,*LinkQueue;
Typedef struct﹛
int size;
Link:Queue rear;
}Queue;
【C函数】
int EnQueue(Queue*Q,KeyType new_elem)
﹛ //元素new_elem 入队列
QNode*p;
P=(QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(!p)
return ERROR;
P->data=new_elem;
if(Q->rear)﹛
P->next=Q->rear->next;
( 1 );
﹜
else
P->next=p;
﹙ 2 ﹚;
Q->size++;
return OK;
﹜
int DeQueue(Queue*Q,KeyType*elem)
﹛ //出队列
QNode*p;
If(0==q->size) //是空队列
Return ERROR;
P=( 3 ); //令p指向队头元素结点
*elem =p->data;
q->rear->next=( 4 ); //将队列元素结点从链表中去除
if(( 5 )) //被删除的队头结点是队列中唯一结点
q->rear=NULL; //变成空队列
free(p);
q->size--;
return OK;
﹜
-
阅读下列说明和C函数,填补函数中的空缺,将解答填入答案纸的对应栏目内。
【说明】
函数isLegal(char*ipaddr)的功能是判断以点分十进制数表示的IPV4地址是否合法。参数ipadddr 给出表示IPV4地址的字符串的首地址,串中仅含数字字符和“.”。若IPV4地址合法则返回1,否则返回0。判定为合法的条件是:每个十进制数的值位于整数区间[0,255],两个相邻的树之间用“.”分隔,共4个数、3个“.”。例如,192.168.0.15、1.0.0.1是合法的,192.168.1.256、1.1..1是不合法的。
【函数】
int isLegal (char*ipaddr)
﹛
int flag;
int curVal; //curVal 表示分析出的一个十进制数
int decNum=0,dotNum=0; //decNum 用于记录十进制数的个数
//dotNum 用户记录点的个数
char*p=( 1 );
for(;*p;p++) ﹛
curVal=0;flag=0
while (isdigit(*p))﹛ //判断是否伟数字字符
curVal=( 2 )+*p-’0’;
( 3 )
flag=1;
﹜
if(curVal>255)﹛
return 0;
﹜
if (flag)﹛
( 4 )
﹜if(*p=’.’﹛
dotNum++;
﹜
﹜
if (( 5) )﹛
return 1;
﹜
return 0;
﹜
-
阅读下列说明和C函数,填补C函数中的空缺,将解答填入答案纸的对应栏目内。
【说明】
字符串是程序中常见的一种处理对象,在字符串中进行子串的定位、插入和删除是常见的运算。
设存储字符串时不设置结束标志,而是另行说明串的长度,因此串类型定义如下:
typedef struct ﹛
Char *str; //字符串存储空间的起始地址
int length; //字符串长
int capacity; //存储空间的容量
﹜SString;
【函数1说明】
函数indexStr(S,T,pos)的功能是:在S 所表示的字符串中,从下标pos开始查找T所表示字符串首次出现的位置。方法是:第一趟从S中下标为pos、T中下标伟0的字符开始,从左往右逐个对于来比较S和T的字符,直到遇到不同的字符或者到达T的末尾。若到达T的末尾,则本趟匹配的起始下标pos为T出现的位置,结束查找;若遇到了不同的字符,则本趟匹配失效。下一趟从S中下标pos+1处的字符开始,重复以上过程。若在S中找到T,则返回其首次出现的位置,否则返回-1。
例如,若S中的字符为伟”students ents”,T中的字符串伟”ent",pos=0,则T在S中首次出现的位置为4。
【C函数1】
int index Str(SString S ,SString T,int pos)
﹛
int i,j:
i (S.length<1||T.length<1||pos+T.length-1)
return-1;
for(i=pos,j=0;i
if (S.str[i]==T.str[j])﹛
i++;j++;
﹜
else﹛
i=( 1 );j=0
﹜
﹜
if ( 2 )return i -T.length;
return-1;
﹜
【函数2说明】
函数 eraseStr(S,T}的功能是删除字符串S中所有与T相同的子串,其处理过程为: 首先从字符串 S 的第一个字符(下标为0)开始查找子串T,若找到〈得到子串在S中的起始位置),则将串 S 中子串T之后的所有字符向前移动,将子串T覆盖,从而将其删除,然后重新开始查找下一个子串T,若找到就用后面的宇符序列进行覆盖,重复上述过程,直到将S中所有的子串T删除。
例如,若字符串 S为 “12ab345abab678”、T为“ab”。第一次找到“ab”时(位置为2),将“345abab678”前移,S 中的串改为“12345abab678” ,第二次找到“ab”时(位置为 5);将“ab678”前移,S中的串改为“12345ab678”,第三次找到“ab”时(位置为5);将“678”前移 ,S中的串改为“12345678 ”。
【C函数2】
Void eraseStr(SString*S,SStringT)
﹛
int i;
int pos;
if (S->length<1||T.length<1||S->length
return;
Pos=0;
for(;;)﹛
//调用indexStr在S所表示串的pos开始查找T的位置
Pos=indexStr( 3 );
if(pos=-1) //S所表示串中不存在子串T
return;
for(i=pos+T.length;i
length;i++) //通过覆盖来删除自串T S->str[( 4 )]=S->str[i];
S->length=( 5 ); //更新S所表示串的长度
﹜
﹜
-
阅读下列说明和流程图,填补流程图中的空缺,将解答填入答题纸的对应栏内。
【说明】
设有二维整数数组(矩阵)A[1:m,1:n],其每行元素从左到右是递增的,每列元素从上到下是递增的。以下流程图旨在该矩阵中需找与给定整数X相等的数。如果找不到则输出“false”;只要找到一个(可能有多个)就输出“True”以及该元素的下标i和j(注意数组元素的下标从1开始)。
例如,在如下矩阵中查找整数8,则输出伟:True,4,1
2 4 6 9
4 5 9 10
6 7 10 12
8 9 11 13
流程图中采用的算法如下:从矩阵的右上角元素开始,按照一定的路线逐个取元素与给定整数X进行比较(必要时向左走一步或向下走一步取下一个元素),直到找到相等的数或超出矩阵范围(找不到)。
【流程图】
【问题】该算法的时间复杂数是()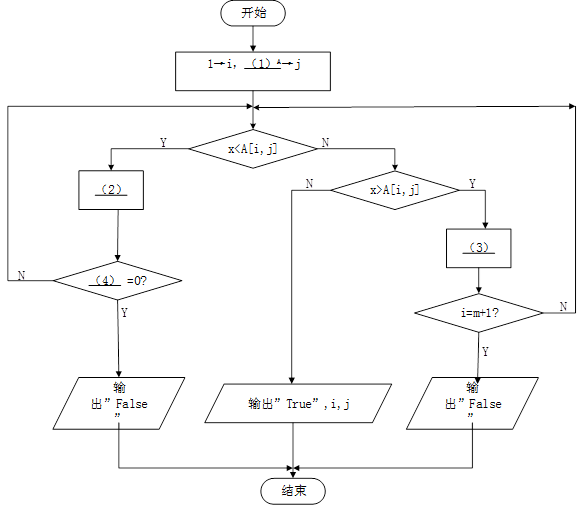
供选择答案:A.O(1) B.O(m+n) C.O(m*n) D,O(m²+n²)
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟练习题之单选题(1
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(2)
高级经济师考试试题精选练习(3)
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟试题及答案
高级经济师考试试题及答案:单选练习题
高级经济师考试试题:经济法案例试题精
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(1)
高级经济师考试模拟题及答案练习(2)



