英语科技文选自考2010年04月真题及答案解析
-
Early Education
-
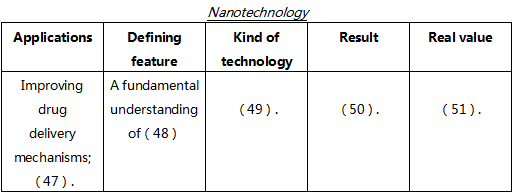
It is increasingly common to hear people referring to “the nanotechnology industry”, just like the software or mobile phone industries, but will such a thing ever exist? Many of the companies working with nanotechnology are simply applying our knowledge of the nanoscale to existing industries, whether it is improving drug delivery mechanisms for the pharmaceutical industry, or producing nanoclay particles for the plastics industry. In fact nanotechnology is an enabling technology rather than an industry in its own right. No one would ever describe Microsoft or Oracle as being part of the electricity industry, even though without electricity the software industry could not exist. Rather, nanotechnology is a fundamental understanding of how nature works at the atomic scale. New industries will be generated as a result of this understanding, just as the understanding of how electrons can be moved in a conductor by applying a potential difference led to electric lighting, the telephone, computing, the internet and many other industries, all of which would not have been possible without it. While it is possible to buy a packet of nanotechnology, a gram of nanotubes for example, it would have zero intrinsic value. The real value of the nanotubes would be in their application, whether within existing industry, or to enable the creation of a whole new one.
-
What the present change will turn out to be will depend on______.
- A.technological innovation in this domain
- B.what social and cultural changes will take place
- C.whether consumers greet this change with enough enthusiasm
- D.all of the above
-
What Peter Cochrane says chiefly means that________.
- A.the future will see electronic people doing most of work for human beings
- B.dramatic changes will take place in our everyday life
- C.humans will be deprived of the sensations of touch,resistance and weight
- D.our minds will be so flooded with information that we may be confused
-
It is implied in the second paragraph that_________.
- A.some people are overenthusiastic about the scale of change digital media willbring us
- B.the speed and scale of change brought to us by the digital media will be dramatic
- C.today’s changes will in no way match the changes taking place between the1880s and the 1930s
- D.no one is sure to what extent digital technology will change the media
-
In terms of the scale of change, the author considers the present change_____.
- A.as a revolution
- B.as being inestimable
- C.as being superficial
- D.as one of the old changes
-
(B)
Futurologists have not been very precise about how, and how much, digital media will change our lives. Most comment has focused on the expectation that consumers will soon be able to use their TV or PC to shop, bank and order movies from their armchair. Commentators envisage more dramatic changes to everyday life. Nicholas Negroponte, director of MIT’ s Media Lab, believes that a key development over the next five years will be the “personalization” of the computer, with wearable devices such as a wrist-mounted TV, computer and telephone. Peter Cochrane, head of research at British Telecom, looks further ahead, asking us to “imagine a virtual reality interface, with your visual cortex flooded by information from spectacle-mounted or contact lenses augmented by directional audio input, tactile gloves and prosthetic arms and fingers that will give you the sensation of touch, resistance and weight”.
Historically, enthusiasts for new technologies have usually been overoptimistic about the speed of change. Most new technologies take longer to be adopted by the general public than these enthusiasts expect, although there have been exceptions: once they had reached critical mass, VCRs and mobile phones took off faster than most experts predicted. Arguably, everyday life in the advanced economies changed more between the 1880s and the 1930s than in the last fifty years or, possibly, the next. Nevertheless, it is valid to talk about a digital “revolution”, since the extent of change is dramatic by any standards and digital technology is its biggest single driving force. Even if the enthusiasts overstate how quickly things will change, they may turn out to be right about the scale of that change.
- At this stage, no one knows how the digital revolution will develop. Although the technology itself is now becoming somewhat more predictable, exactly how, and how fast, things change will depend not only on technological developments but also on the poli
- A.The likely impact of digital technology on everyday life.
- B.The improvements made in me world of mass communication.
- C.The applications of digital media in businesses and our lives.
- D.The overoptimistic feeings people hold about the new technologies.
-
Which of the following statements best describes the conclusion of the severaldifferent experiments?
- A.Lipid droplets were almost absent.
- B.Drugs can be developed to regulate the expression of FIT genes.
- C.Lipid droplets can be increased or reduced by different expressions of FIT genes.
- D.FIT genes induce lipid droplet accumulation in cells.
-
What is the one of the implications of the discovery of FIT genes?
- A.Drugs can thus be developed to help to keep to a sensible body weight.
- B.Drugs can thus be developed to effectively palliate diseases arising from obesity.
- C.Diabetes can be cured.
- D.Heart disease can be warded off.
-
What can be said about FIT1 and FIT2 according to the passage?
- A.Cells with their suppressed expression have more lipid droplets.
- B.Cells with their over-expression have fewer lipid droplets.
- C.They are different from other gene families.
- D.They are more similar than different to each other.
外贸函电2008年7月真题试题及答案
外贸函电2009年4月真题试题及答案
外贸函电2009年7月真题试题及答案
外贸函电2010年4月真题试题及答案
外贸函电2010年7月真题试题及答案
外贸函电2011年4月真题试题及答案
外贸函电2011年7月真题试题及答案
外贸函电2012年4月真题试题及答案
外贸函电2012年7月真题试题及答案
外贸函电2013年4月真题试题及答案
