算法f31的功能是清空带头结点的链队列Q请在空缺处填入合适的内容,使其成为一个完整的算法。
typedef struct node{
DataType data;
struct node next;
} QueueNode;
typedef struct{
QueueNode *front;//队头指针
QueueNode rear;//队尾指针
}LinkQueue;
void f31(LinkQueue*Q)
{
QueueNode *P,*
P=(1)
while(p! =NULL)
s=p
p=p->next;
free(s):
}
(2) =NULLI
Q->rear=(3)
}
(1)
(2)
(3)
-
假设以二叉链表作为二叉树的存储结构,其结点结构为:

照如下给定的函数f34的原型,编写求二叉树中叶子结点所在的最小层次与最大层次的函数。其中,参数 level为函数执行过程中T当前所指结点的层次,其初值为1;lmin与max分别为叶子结点的最小层次与最大层次,它们的初值均为0void f34(BinTree T, int level, int *Imin, int *Imax);
-
二叉排序树的存储结构定义为以下类型
typedef int KeyType;
typedef struct node{
KeyType key;//关键字项
InfoType otherinfo;//其他数据项
struct node Ichild, rchild//左右孩子指针
BSTNode, *BSTree;
阅读算法f33,并回答问题:
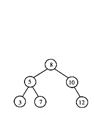
(1)对如题图所示的二叉排序树T,写出33(T,8)返回的指针所指结点的关键字
(2)在哪些情况下算法f33返回空指针?
(3)简述算法f33的功能。
BSTNode f333(BSTree, KeyType)
{BSTNode *p:
if (T==NULL) return NULL:
p=f33(T->lchild, x);
if (p!-NULL) return pi
if (T->key >x) return T:
return f33(T->rchild, x);
}
(1)
(2)
(3)
-
下列程序判断字符串s是否对称,对称则返回1,否则返回0;如f("abba")返回1,f(abab")返回0;在空缺处填写相应的语句。
int f((1))
while (sj]) (2)
for(j-; i
return (3)
}
(1)
(2)
(3)
-
(1)对于下列图G的邻接矩阵,写出函数调用f32(&G,3)的返回值

int f32(MGraph G, int i)
{int d=,j;
for(j=0,j
++) {if(G->edges[]) d++;
if(G->edges[]) d++;
}
return d;
}
(1)
(2)
(3)
(2)简述函数f32的功能。
(3)写出函数f32的时间复杂度
-
算法f31的功能是清空带头结点的链队列Q请在空缺处填入合适的内容,使其成为一个完整的算法。
typedef struct node{
DataType data;
struct node next;
} QueueNode;
typedef struct{
QueueNode *front;//队头指针
QueueNode rear;//队尾指针
}LinkQueue;
void f31(LinkQueue*Q)
{
QueueNode *P,*
P=(1)
while(p! =NULL)
s=p
p=p->next;
free(s):
}
(2) =NULLI
Q->rear=(3)
}
(1)
(2)
(3)
-
试举一个数据结构的例子,叙述其逻辑结构存储结构两方面的内容
-
由字符集{s,t,ae,i}及其在电文中出现的频度构建的哈夫曼树如题27图所示。已知某段电文的哈夫曼编码为1110000100,请根据该哈夫曼树进行译码,写出原来的电文。
-
图G=(V,E),其中:V={0,1,2,3,4,5},E={<0,1>,<0,2>,<1,4>,<2,5>,<5,4><4,3>,<5,3>试写出图G中顶点的所有拓扑排序。
-
对序列(48,37,63,96,22,31,50,55,11进行堆排序,写出构建的初始(大根)堆及前两趟重建堆之后的序列状态。
-
队列只允许在表的一端进行插入,而在另一端进行删除,允许删除的一端称为( )允许插入的一端称为( )
2005年初级经济师考试《旅游经济专
初级旅游经济师试题及答案一
初级旅游经济师试题及答案二
2005年初级经济师考试《邮电经济专
初级经济师试题及答案1(邮电经济)
初级经济师试题及答案1(保险经济)
初级经济师试题及答案2(邮电经济)
初级经济师试题及答案2(保险经济)
初级经济师试题及答案3(保险经济)
2014年经济师初级考试真题《建筑经

