外语教学法2014年4月真题试卷(00833)
-
By the end of the 1960s, the Audiolingual Method became the target of criticism from all sides. However, its contributions to language teaching must not be ignoreD.Please briefly write out the 5 aspects of its contributions.
-
In Chomsky’s idea, a native speaker of a language is said to be equipped with linguistic competence. So what is he supposed to be able to do?
-
In the Oral Approach, what is the teacher required to be? And how does he or she help the students to build up correct language habits?
-
For what purposes does a Grammar-translation teacher employ translation in teaching a foreign language?
-
What are the objectives of the Direct Method?
-
What is the role of the teacher in the Total Physical Response?
-
According to Morrow, what are the features of real communicative activities?
-
How is the Natural Approach towards the learners’error?
-
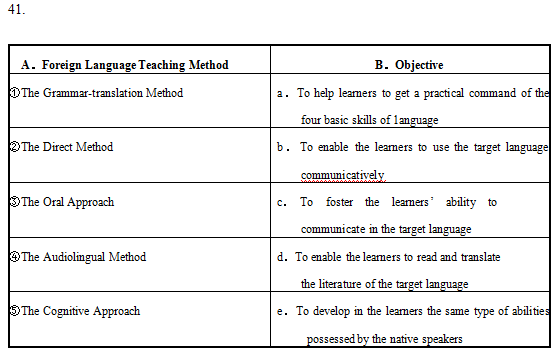
-

-
According to Piaget, thought or thinking has its origin in actions physically performed and then ______.
-
A group of German psychologists used the word Gestalt, which is approximately in the meaning of “_______ shape” to name their school of psychology.
-
The cognitive theory suggests that language acquisition involves constant practice until ______is achieved.
-
According to behaviorists, learning consists of stimulus-response ______ , and is described as the formation of association between responses.
-
______activities require the learners to take part in communication which involves personal experience and emotions.
-
The Notional-functional syllabus focuses on ______ as the organizing elements of English curricula, whereas the structural syllabus regards grammatical structures as the organizers.
-
One impetus for the procedures of grammar analysis and translation in teaching Latin was brought about by the ______ needs of European countries.
-
The Natural Approach holds that learned language knowledge has primarily a ______ function.
-
The affective filter hypothesis identifies self-confidence, ______ and anxiety as the three affective variables related to second language acquisition.
-
When teaching grammar in the Oral Approach, the teacher usually helps the students to learn some grammatical points over a relatively long time instead of giving them a heavy indigestible dose of ______.
-
In his research of the theory of systemic linguistics, Halliday made outstanding achievements in the study of ______.
-
The Cognitive Approach holds that learning a language is a process of acquiring ______ control of the phonological, grammatical and lexical patterns of a second language, largely through study and analysis of these patterns as a body of knowledge.
-
The learning of a foreign language was viewed by the Direct Methodologists as analogous to the language ______ , and the learning processes involved were often interpreted in terms of an associationist psychology.
-
Krashen and Terrell believe that language skills acquired through ______ transfer to other skills.
-
Although the teaching of all the four language skills is advocated by most Direct Methodologists, ______ communication skills are regarded as basic.
-
The structural linguists believe that the primary medium of language is ______.
-
In a Total Physical Response classroom, the students listen attentively and respond ______ to commands given by the teacher.
-
Suggestopaedia, the application of the study of ______ to pedagogy, has been developed to help students eliminate the feeling that they cannot be successful and, thus to help them overcome the barriers to learning.
-
Most of the teaching activities in a Grammar-translation classroom serve the purpose of mastering ______ rules.
-
______ refers to any information that learners receive from the teacher or others concerning their communication.
-
According to D.Ausubel, the principal function of ______ is to act as a bridge between what learners already know and what they need to know.
- A.schema theory
- B.language acquisition device
- C.language competence
- D.advance organizers
-
According to cognitive psychologists, learning involves ______ representations that offer regulation and guidance for the performance.
- A.complicated
- B.simple
- C.internal
- D.external
-
The procedures and techniques proposed by the Natural Approach are ______ in the field of language teaching.
- A.not new
- B.revolutionary
- C.radical
- D.innovative
-
Krashen and Terrell equate the Natural Approach with ______.
- A.the Communicative Approach
- B.the Cognitive Approach
- C.the Total Physical Response
- D.the Community Language Learning
-
The Communicative Approach has been developed particularly by ______ applied linguists.
- A.French
- B.Canadian
- C.British
- D.American
-
The use of drills and ______ is a distinctive feature of the Audiolingual method.
- A.pair-work
- B.pattern practice
- C.dictation
- D.questions and answers
-
People advocating the Oral Approach believed that students tend to find it ______ to internalize the grammatical rules with the help of the situation provided.
- A.easy
- B.difficult
- C.possible
- D.impossible
-
______ is regarded as the source of the students' ability to use the language in structured interactions.
- A.Vocabulary
- B.Acquisition
- C.Grammar
- D.Learning
-
When the teacher in a communicative class is answering students' questions and monitoring their performance, he/she is playing the role of a(n)______.
- A.manager
- B.facilitator
- C.co-communicator
- D.advisor
-
Pragmatics is the study of______ .
- A.how sentences in spoken and written language form larger meaningful units
- B.the use of language in communication
- C.the meanings of words and sentences
- D.the grammatical arrangement of words in sentences
-
Foreign language teaching involves quite a number of disciplines EXCEPT______.
- A.psycholinguistics
- B.psychology
- C.sociology
- D.sociolinguistics
-
The ______ , known variously as the Aural-oral Approach and the Structural Approach, influenced the way languages were taught in the US and elsewhere in the world throughout the 1950s.
- A.Audiolingual Method
- B.Cognitive Approach
- C.Direct Method
- D.Oral Approach
-
The Direct Method emerged as a result of _____ in the 19th century.
- A.classroom instruction
- B.mass production
- C.communicative needs
- D.language teaching innovations
-
As a key feature of the Oral Approach,______ should be presented in sentences, which should be practiced in meaningful contexts.
- A.words
- B.phrases
- C.paragraphs
- D.vocabulary
-
The technique used by a Grammar-translation teacher is ______ teaching of grammar.
- A.inductive
- B.deductive
- C.indirect
- D.direct
-
The Silent Way is an approach to language teaching developed in the United States, principally by ______.
- A.James Asher
- B.Caleb Gattegno
- C.Charles A. Curran
- D.Georgi Lozanov
-
The generative-transformational school of linguistics emerged through the influence of ______.
- A.J. B.Bruner
- B.N. Chomsky
- C.D.Ausubel
- D.G. Kelly
-
When was the Direct Method developed as a reaction against the Grammar-translation Method?
- A.In the late 19th century.
- B.In the early 20th century.
- C.In the mid-19th century.
- D.In the early 19th century.
-
Foreign language teachers usually adopted the strategy of combining grammar rules with______in the 19th century.
- A.translating
- B.explaining
- C.analyzing
- D.composing
-
Who is the advocate of the Total Physical Response?
- A.James Asher
- B.Caleb Gattegno
- C.Charles A. Curran
- D.Georgi Lozanov

